Support center +91 97257 89197
Generative AI developmentAugust 27, 2024
AI-Powered Automation in Logistics: The Future of Smart Warehousing

Introduction
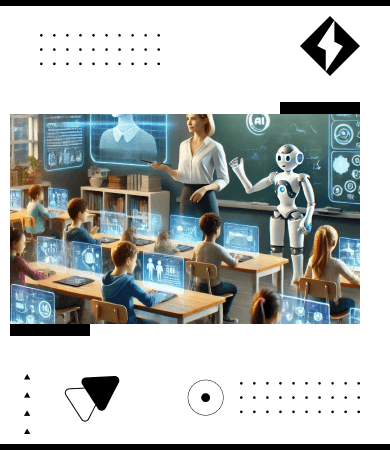
The logistics industry is undergoing a transformation, and at the heart of this change is the rise of smart warehousing powered by artificial intelligence (AI). In an era where speed, accuracy, and efficiency are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge, businesses are looking to AI to revolutionize the way their warehouses operate. Smart warehousing refers to the integration of advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to automate and optimize warehousing operations. This shift marks a significant departure from traditional manual processes, offering a glimpse into the future of logistics.
As customer expectations for faster deliveries and lower costs increase, logistics providers must adopt technologies that allow them to meet demand while maintaining profitability. AI-powered automation is not just an option—it's quickly becoming a necessity. In this post, we will explore the key technologies driving smart warehousing, their benefits, challenges, and what the future holds for logistics and warehousing as AI continues to evolve.
The Role of AI in Logistics
AI has already started making a significant impact across various industries, and logistics is no exception. In the realm of warehousing, AI is used to automate complex processes, improve decision-making, and predict future trends. Unlike traditional warehouses, which rely heavily on manual labor and simple automation, smart warehouses leverage AI to create an interconnected system where machines and algorithms work together to streamline operations.
Key AI technologies used in logistics include machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing (NLP). Machine learning algorithms enable predictive analytics, helping businesses forecast demand, optimize stock levels, and manage supply chains more effectively. Computer vision is used to enable machines to "see" and recognize objects, facilitating tasks like inventory tracking and quality control. NLP allows AI systems to communicate with human operators or interpret commands from voice-controlled systems, improving overall efficiency.
These technologies work in unison to create a system where warehouses can operate more autonomously, reducing the need for human intervention. For example, a machine learning algorithm could predict when a particular product will be in high demand, prompting the system to reorder inventory in advance. Meanwhile, robotic systems equipped with computer vision can automatically pick and pack items, minimizing human error.
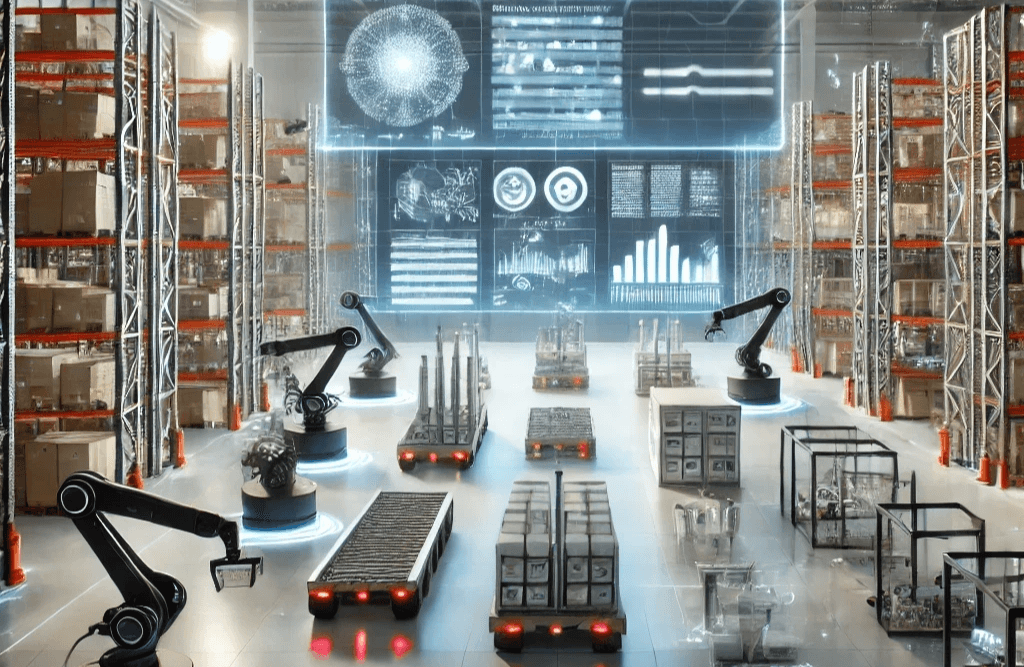
Key Components of AI-Powered Smart Warehousing
- Robotics and Automation The use of robots in warehousing has seen a significant increase, with companies like Amazon leading the charge in integrating robotic systems to manage their logistics operations. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), robotic arms, and drones are now commonly used to move inventory, pick items, and monitor stock levels. These robots not only work faster than human workers but are also capable of operating 24/7, significantly boosting productivity.
Case Study: Amazon’s Robotic Warehouses: Amazon is a prime example of a company that has embraced AI-powered automation in its warehousing operations. Using robots designed by its subsidiary, Amazon Robotics, the company’s warehouses are equipped with mobile robots that can transport items across vast distances, reducing the time it takes for human workers to pick and pack products. These robots work alongside human employees, allowing for a more efficient and faster fulfillment process.
- AI-Powered Inventory Management Inventory management is one of the most crucial aspects of warehousing. Keeping track of stock levels, ensuring the availability of products, and predicting future demand can be overwhelming, especially for large-scale operations. AI plays a pivotal role in optimizing these processes. With predictive analytics, AI systems can forecast demand trends, allowing warehouses to maintain optimal stock levels without overordering or understocking.
Real-time inventory tracking is another game-changer in smart warehousing. By integrating IoT devices such as RFID tags and smart sensors, AI systems can monitor inventory in real-time. This enables managers to know exactly where each product is located, when it was last moved, and how much stock remains—all without manual intervention.
- Smart Data Analytics for Supply Chain Optimization AI-driven data analytics offers invaluable insights that can improve overall supply chain performance. By analyzing vast amounts of data from multiple sources—such as shipping patterns, customer orders, and external market conditions—AI systems can make more informed decisions about logistics operations. This can lead to more efficient route planning, better inventory management, and ultimately, cost savings for businesses.
For example, AI can analyze weather patterns and traffic conditions to predict delivery delays, allowing businesses to reroute shipments or adjust schedules to avoid bottlenecks. AI-driven insights can also help optimize warehouse layout, ensuring that high-demand products are stored in easily accessible areas, reducing the time it takes to fulfill orders.
- AI in Warehouse Layout and Design The physical layout of a warehouse plays a critical role in its overall efficiency. Traditional warehouses are often designed based on fixed parameters, which don’t change over time. However, AI-powered systems can analyze a warehouse’s layout and make adjustments to improve efficiency. Machine learning algorithms can study historical data on product movements, identifying the most frequently accessed areas and suggesting new configurations to minimize unnecessary travel time.
This dynamic approach to warehouse layout design can significantly reduce the time it takes for products to be picked, packed, and shipped, further enhancing the overall efficiency of the operation.
Benefits of AI-Powered Automation in Warehousing
-
Increased Efficiency One of the most significant benefits of AI-powered automation in warehousing is the dramatic increase in efficiency. Robots can operate around the clock, ensuring that tasks such as picking, sorting, and packing are completed much faster than if done manually. AI systems also help optimize warehouse operations by predicting demand, enabling warehouses to maintain optimal stock levels and avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
-
Cost Reduction While the initial investment in AI technology can be high, the long-term cost savings are substantial. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can reduce their reliance on manual labor, leading to lower staffing costs. Additionally, AI-powered systems minimize human error, reducing the cost associated with mistakes such as incorrect orders or lost inventory.
-
Improved Accuracy and Reliability Human error is one of the leading causes of inefficiencies in traditional warehouses. Misplacing items, picking the wrong product, or failing to update inventory records are common mistakes that can slow down operations. AI-powered systems, on the other hand, rely on data and algorithms to perform these tasks, resulting in greater accuracy and reliability. Whether it's using robots to pick items or AI-driven analytics to predict stock levels, smart warehouses operate with a level of precision that significantly reduces errors.
-
Enhanced Safety Warehousing can be a dangerous environment, especially in large-scale operations with heavy machinery and complex processes. AI-driven robots and drones can take over many of the more dangerous tasks, such as lifting heavy loads or working in hazardous environments, reducing the risk of injury to human workers. Additionally, AI systems can monitor warehouse conditions in real-time, alerting managers to potential safety hazards before they become critical issues.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of AI-powered automation in warehousing are clear, it’s important to recognize the challenges and considerations that come with implementing such advanced technologies. Transitioning from a traditional warehouse to a smart warehouse is not without obstacles, and businesses need to be aware of the following factors before adopting AI-driven solutions.
- Implementation Costs The upfront costs of implementing AI technologies in warehouses can be significant. Between purchasing robots, installing sensors, developing AI software, and integrating these systems into existing operations, the initial investment can be high. Smaller businesses, in particular, may struggle with these costs, making it challenging to keep up with larger competitors who have the resources to fully automate their logistics processes.
However, while the initial capital expenditure may be steep, the long-term savings in labor costs, increased efficiency, and reduction in errors often justify the investment. Many companies recoup their costs within a few years as AI streamlines operations, boosts productivity, and reduces operational inefficiencies.
- Workforce Adaptation and Displacement One of the major concerns surrounding AI and automation is the impact on the workforce. As warehouses become more automated, the demand for traditional warehouse jobs—like pickers and packers—declines. This shift can lead to workforce displacement, which raises social and economic concerns. Workers who have spent years in manual roles may find themselves needing to retrain or seek employment elsewhere.
However, AI is not just about replacing jobs—it’s also about creating new opportunities. As warehouses adopt AI systems, there will be a growing need for workers skilled in managing and maintaining these technologies. The rise of smart warehouses creates opportunities for roles in AI oversight, robotics maintenance, data analysis, and system integration. Businesses that are mindful of workforce displacement can help transition their employees to new roles through retraining programs.
- Cybersecurity Risks The increased reliance on AI, IoT devices, and cloud-based systems introduces new cybersecurity risks. Smart warehouses are highly connected environments, where data is constantly being transmitted between machines, sensors, and AI systems. While this connectivity is essential for smooth operations, it also opens up potential vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit.
A cyberattack on a smart warehouse could disrupt operations, lead to data theft, or even shut down the entire system. To mitigate these risks, companies must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, encryption, and regular system audits. Moreover, businesses must comply with data privacy regulations to ensure that sensitive customer and operational data is protected.
- Regulatory Compliance As AI and automation technologies evolve, so too do the regulations governing their use. Smart warehouses must adhere to various industry standards, particularly when it comes to data handling and employee safety. For example, regulations surrounding the use of autonomous vehicles in warehouses, or compliance with GDPR for handling customer data, may present additional challenges.
Staying compliant with these regulations requires ongoing investment in legal advice, system upgrades, and employee training. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal action, and damage to a company’s reputation.
Future Trends in AI-Powered Smart Warehousing
The future of logistics and warehousing is set to be shaped by even more advanced AI technologies and automation solutions. Here are some of the trends we can expect to see in the coming years:
- The Rise of Autonomous Vehicles in Logistics While automation inside the warehouse is already underway, the next big leap for logistics will involve autonomous vehicles that operate outside the warehouse as well. Self-driving trucks, drones for last-mile deliveries, and autonomous delivery vehicles are set to revolutionize how goods are transported from the warehouse to the customer.
Companies like Waymo and Tesla are developing autonomous trucks that could eliminate the need for human drivers in long-haul logistics, dramatically reducing delivery times and costs. Drones, on the other hand, could be used for rapid delivery in urban areas, where traditional delivery trucks may be inefficient or impractical.
- AI-Driven Sustainability Initiatives As businesses face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, AI-powered warehouses will play a critical role in reducing the carbon footprint of logistics operations. AI systems can optimize energy usage in warehouses by analyzing patterns in energy consumption and adjusting heating, cooling, and lighting accordingly.
Additionally, AI-driven data analytics can help logistics companies reduce waste in their supply chains. For example, AI can identify inefficiencies in the movement of goods, such as unnecessary transportation steps, and suggest more eco-friendly alternatives. This push towards greener logistics is not only good for the environment but also enhances a company’s reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
- Human-AI Collaboration Rather than replacing human workers entirely, the future of smart warehousing will involve increasing collaboration between humans and AI. Workers will use AI-powered tools to enhance their decision-making and productivity, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks while automation handles repetitive or dangerous jobs.
Augmented reality (AR) tools, for example, could be used by warehouse employees to receive real-time instructions from AI systems. These tools could help workers find items more quickly, repair faulty machines, or monitor warehouse operations from a central hub. By combining human creativity with AI’s processing power, businesses can create more efficient and innovative workflows.
- 5G Connectivity for Enhanced Operations The rollout of 5G networks will further enhance smart warehouse operations. With faster data transmission speeds and lower latency, 5G will enable real-time communication between all devices in a smart warehouse. This will result in even more seamless integration of robotics, IoT sensors, and AI systems, allowing for more precise and instantaneous decision-making.
5G will also support advanced AI applications that require large amounts of data to be processed in real time, such as advanced predictive analytics and AI-driven maintenance systems. With 5G, smart warehouses will be able to operate more efficiently and react to changes in demand, inventory, or environmental conditions more quickly.
Conclusion
AI-powered automation is undeniably shaping the future of logistics and smart warehousing. From the use of robotics to optimize daily operations, to predictive analytics for inventory management, and autonomous vehicles for transport, AI is revolutionizing every aspect of warehousing. Businesses that embrace AI technologies will be able to operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and improve accuracy, ultimately gaining a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
However, the transition to AI-powered smart warehousing is not without challenges. Businesses must carefully consider the costs, workforce implications, and cybersecurity risks. By addressing these challenges proactively and investing in AI solutions, companies can position themselves for success in the rapidly evolving logistics industry.
As AI continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative solutions to emerge, paving the way for fully autonomous, highly efficient, and sustainable smart warehouses. The future of logistics is bright for those willing to embrace the change.
TLDR
AI-powered automation is revolutionizing logistics and transforming traditional warehousing into smart, highly efficient operations. With AI technologies like robotics, predictive analytics, and smart inventory management, businesses can reduce costs, improve accuracy, and enhance safety in their warehouses. However, challenges such as high implementation costs and cybersecurity risks must be addressed. As AI continues to advance, smart warehousing will play a critical role in the future of logistics.
FAQs
AI-powered smart warehousing refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies such as machine learning, robotics, and predictive analytics to automate and optimize warehouse operations. This includes real-time inventory management, automated sorting, and robotic assistance, leading to more efficient and accurate processes.
AI enhances warehouse efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, such as picking and sorting, and enabling real-time tracking of inventory. It also optimizes supply chain operations using predictive analytics, helping businesses forecast demand more accurately and allocate resources better.
The main benefits include cost reduction, improved accuracy, faster processing times, and enhanced safety. AI-driven automation reduces the need for manual labor, minimizes errors in inventory management, and ensures that dangerous tasks are handled by robots, improving worker safety.
The biggest challenges include the high upfront costs of AI technologies, the need to retrain employees to work with new systems, and potential cybersecurity risks due to the increased reliance on data and connectivity. Additionally, adhering to data privacy regulations can add complexity.
The future of AI in logistics will likely involve more advanced autonomous vehicles, smarter inventory management systems, and sustainable practices driven by AI. Human-AI collaboration will also increase, as workers will increasingly rely on AI tools to enhance their productivity and decision-making.
Work with us